Page 3 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 3
CHAPTER 12 • FEMOROPOPLITEAL ARTERIAL DISEASE
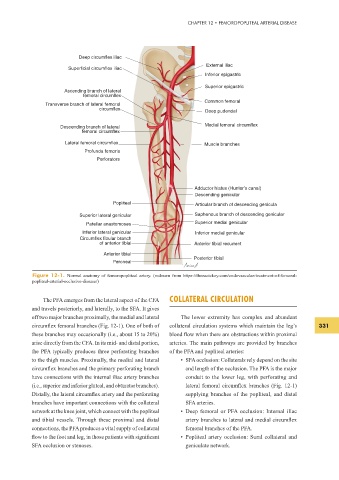
Deep circumflex iliac
External iliac
Superficial circumflex iliac
Inferior epigastric
Superior epigastric
Ascending branch of lateral
femoral circumflex
Common femoral
Transverse branch of lateral femoral
circumflex
Deep pudendal
Medial femoral circumflex
Descending branch of lateral
femoral circumflex
Lateral femoral circumflex Muscle branches
Profunda femoris
Perforators
Adductor hiatus (Hunter’s canal)
Descending genicular
Popliteal Articular branch of descending genicula
Superior lateral genicular Saphenous branch of descending genicular
Patellar anastomoses Superior medial genicular
Inferior lateral genicular Inferior medial genicular
Circumflex fibular branch
of anterior tibial Anterior tibial recurrent
Anterior tibial
Posterior tibial
Peroneal
Figure 12-1. Normal anatomy of femoropopliteal artery. (redrawn from https://thoracickey.com/endovascular-treatment-of-femoral-
popliteal-arterial-occlusive-disease/)
The PFA emerges from the lateral aspect of the CFA COLLATERAL CIRCULATION
and travels posteriorly, and laterally, to the SFA. It gives
off two major branches proximally, the medial and lateral The lower extremity has complex and abundant
circumf ex femoral branches (Fig. 12-1). One of both of collateral circulation systems which maintain the leg’s 331
these branches may occasionally (i.e., about 15 to 20%) blood f ow when there are obstructions within proximal
arise directly from the CFA. In its mid- and distal portion, arteries. The main pathways are provided by branches
the PFA typically produces three perforating branches of the PFA and popliteal arteries:
to the thigh muscles. Proximally, the medial and lateral • SFA occlusion: Collaterals rely depend on the site
circumf ex branches and the primary perforating branch and length of the occlusion. The PFA is the major
have connections with the internal iliac artery branches conduit to the lower leg, with perforating and
(i.e., superior and inferior gluteal, and obturator branches). lateral femoral circumf ex branches (Fig. 12-1)
Distally, the lateral circumf ex artery and the perforating supplying branches of the popliteal, and distal
branches have important connections with the collateral SFA arteries.
network at the knee joint, which connect with the popliteal • Deep femoral or PFA occlusion: Internal iliac
and tibial vessels. Through these proximal and distal artery branches to lateral and medial circumf ex
connections, the PFA produces a vital supply of collateral femoral branches of the PFA.
f ow to the foot and leg, in those patients with signif cant • Popliteal artery occlusion: Sural collateral and
SFA occlusion or stenoses. geniculate network.