Page 11 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 11
CHAPTER 10 • RENAL ARTERY INTERVENTION
B arise between the mid L1 and the mid L2 level as well as
accessory renal arteries if present.
The angle for the origin of the renal arteries from the
aorta is important since frequently an anterior-posterior
(AP) angiogram fails to display an ostial lesion accurately.
Unwarranted stent extension into the aorta or geographic miss
with a f oating stent positioned within the post-stenotic segment
can occur if not clearly def ned. In the transverse plane the origin
for the right renal artery has a tendency to be anterolateral,
and the origin of the left renal artery tends to be posterolateral
or lateral (44). If non-selective abdominal angiography is
performed, then it is better to position a catheter in the L1
level to conduct imaging in a 20° LAO projection (Fig. 10-9).
When selective angiography is conducted, then obliquity
should be customized as explained above; and when the
A mid to distal portion of the renal artery has to be visualized,
use of an ipsilateral oblique projection is recommended.
Figure 10-7. Two different vascular access approaches for renal To engage the renal arteries selectively, the angle
artery intervention. A: Femoral approach. B: Radial or brachial approach.
by which the renal artery comes off the aorta determines
the choices of diagnostic catheters. The three types of
DIAGNOSTIC ANGIOGRAPHY take-off angulation include horizontal, downward (or
caudal), or upward (Fig. 10-10). If renal arteries take-off
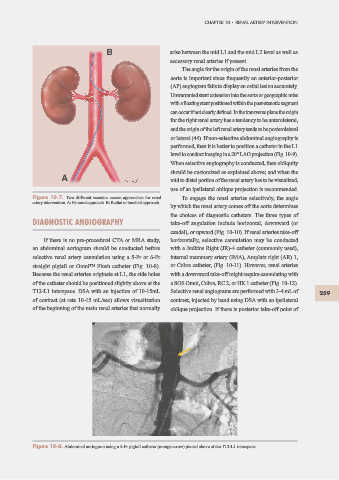
If there is no pre-procedural CTA or MRA study, horizontally, selective cannulation may be conducted
an abdominal aortogram should be conducted before with a Judkins Right (JR)-4 catheter (commonly used),
selective renal artery cannulation using a 5-Fr or 6-Fr internal mammary artery (IMA), Amplatz right (AR) 1,
straight pigtail or Omni™ Flush catheter (Fig. 10-8). or Cobra catheter, (Fig. 10-11). However, renal arteries
Because the renal arteries originate at L1, the side holes with a downward take-off might require cannulating with
of the catheter should be positioned slightly above at the a SOS Omni, Cobra, RC 2, or HK 1 catheter (Fig. 10-12).
T12-L1 interspace. DSA with an injection of 10-15mL Selective renal angiograms are performed with 3-4 mL of 259
of contrast (at rate 10-15 mL/sec) allows visualization contrast, injected by hand using DSA with an ipsilateral
of the beginning of the main renal arteries that normally oblique projection. If there is posterior take-off point of
Figure 10-8. Abdominal aortogram using a 5-Fr pigtail catheter (orange arrow) placed above at the T12-L1 interspace.