Page 6 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 6
CAROTID AND PERIPHERAL VASCULAR INTERVENTIONS: STEP-BY-STEP
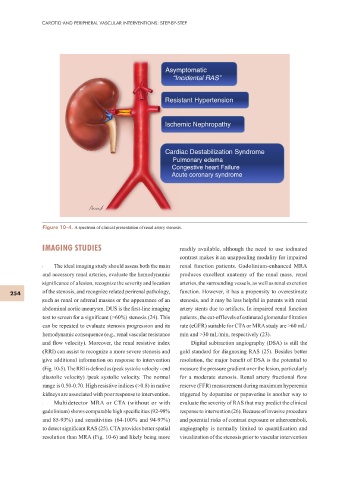
Asymptomatic
“Incidental RAS”
Resistant Hypertension
Ischemic Nephropathy
Cardiac Destabilization Syndrome
Pulmonary edema
Congestive heart Failure
Acute coronary syndrome
Figure 10-4. A spectrum of clinical presentation of renal artery stenosis.
IMAGING STUDIES readily available, although the need to use iodinated
contrast makes it an unappealing modality for impaired
The ideal imaging study should assess both the main renal function patients. Gadolinium-enhanced MRA
and accessory renal arteries, evaluate the hemodynamic produces excellent anatomy of the renal mass, renal
signif cance of a lesion, recognize the severity and location arteries, the surrounding vessels, as well as renal excretion
254 of the stenosis, and recognize related perirenal pathology, function. However, it has a propensity to overestimate
such as renal or adrenal masses or the appearance of an stenosis, and it may be less helpful in patents with renal
abdominal aortic aneurysm. DUS is the f rst-line imaging artery stents due to artifacts. In impaired renal function
test to screen for a signif cant (>60%) stenosis (24). This patients , the cut-off levels of estimated glomerular f ltration
can be repeated to evaluate stenosis progression and its rate (eGFR) suitable for CTA or MRA study are >60 mL/
hemodynamic consequence (e.g., renal vascular resistance min and >30 mL/min, respectively (23).
and f ow velocity). Moreover, the renal resistive index Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is still the
(RRI) can assist to recognize a more severe stenosis and gold standard for diagnosing RAS (25). Besides better
give additional information on response to intervention resolution, the major benef t of DSA is the potential to
(Fig. 10-5). The RRI is def ned as (peak systolic velocity - end measure the pressure gradient over the lesion, particularly
diastolic velocity) /peak systolic velocity. The normal for a moderate stenosis. Renal artery fractional f ow
range is 0.50-0.70. High resistive indices (>0.8) in native reserve (FFR) measurement during maximum hyperemia
kidneys are associated with poor response to intervention. triggered by dopamine or papaverine is another way to
Multidetector MRA or CTA (without or with evaluate the severity of RAS that may predict the clinical
gadolinium) shows comparable high specif cities (92-98% response to intervention (26). Because of invasive procedure
and 85-93%) and sensitivities (64-100% and 94-97%) and potential risks of contrast exposure or atheroemboli,
to detect signif cant RAS (25). CTA provides better spatial angiography is normally limited to quantif cation and
resolution than MRA (Fig. 10-6) and likely being more visualization of the stenosis prior to vascular intervention