Page 7 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 7
CHAPTER 10 • RENAL ARTERY INTERVENTION
or to clarify inconclusive results from noninvasive study. (ARBs)] are effective for managing hypertension
Venous renin measurements, plasma renin measurements associated with renal artery disease and can cause slowing
before and after angiotensin converting enzymes inhibitor of its progression. In two observational studies ARBs and
(ACEI) provocation, and renal scintigraphy are no longer ACEIs have shown advantages in decreasing morbidity and
used for diagnosing atherosclerotic RAS (1,23,27). mortality in RAS patients (32,33). However, these drugs
may decrease glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
TREATMENT and result in a transient reduction in eGFR and increase
serum creatinine. From the 2017 ESC guidelines (23),
Patients with RAS with or without end-stage CKD ACEIs or ARBs are recommended for hypertension
have a shortened life expectancy (28). Most of them treatment related to unilateral RAS. ARBs or ACEIs can
died from acute CV events (29). Risk factor assessment, also be administered in bilateral severe RAS as well as
life-style modif cation, and medications (e.g., antiplatelet a single functioning kidney stenosis if well-tolerated with
and statin) are important and should follow current close observation. Nearly all patients having signif cant
guidelines of primary prevention for CAD (30,31). Most RAS tolerate ARBs or ACEIs without any problem.
antihypertensive drugs [diuretics, beta-blockers, calcium However, optimal target blood pressure (BP) for the setting
channel blockers, and ACEIs, angiotensin renin blockers of RAS, is still unknown.
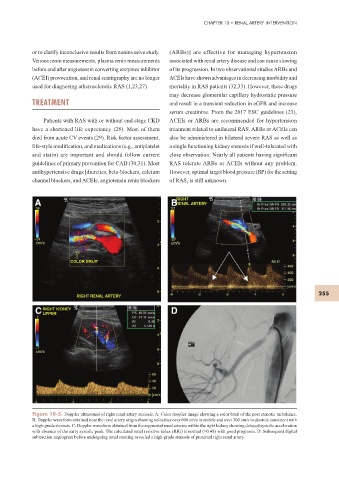
A B
255
C D
Figure 10-5. Doppler ultrasound of right renal artery stenosis. A: Color doppler image showing a color bruit of the post stenotic turbulence.
B: Doppler waveform obtained near the renal artery origin showing velocities over 600 cm/s in systole and over 300 cm/s in diastole consistent with
a high-grade stenosis. C: Doppler waveform obtained from the segmental renal arteries within the right kidney showing delayed systolic acceleration
with absence of the early systolic peak. The calculated renal resistive index (RRI) is normal (=0.48) with good prognosis. D: Subsequent digital
subtraction angiogram before undergoing renal stenting revealed a high-grade stenosis of proximal right renal artery.