Page 11 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 11
CHAPTER 6 • CAROTID ARTERY DISEASE
To conf rm the diagnosis, a complete physical study is crucial to evaluate the structural pathology
examination and neurological assessment is important, and anatomy for the brain and carotid artery, and to guide
including the examination of heart rhythm, auscultation treatment. A duplex ultrasound study (DUS), computed
for carotid bruits and heart murmur (to rule out cardiac tomographic angiography (CTA) and/or magnetic
emboli), fundoscopic examination (for detecting retinal resonance angiography (MRA) are recommended
embolization), together with a focused neurologic examination methods for assessing the severity of extracranial carotid
(to associate with an ischemic territory). The National stenoses (27).
Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) may be applied A DUS is normally the f rst-choice imaging modality
for quantif cation of the neurological def cit and speculate for detecting, grading, and monitoring of extracranial
the outcome after ischemic stroke (25,26). Again, clinical ICA stenoses. The key variables to determine the severity
f ndings have to be associated with vascular and brain of carotid stenosis are the ICA peak systolic velocity
imaging in order to decide if a carotid stenosis is symptomatic. (PSV), ICA end diastolic velocity (EDV), and the ratio
Carotid artery stenosis is def ned as ‘asymptomatic’ of PSV of the ICA to that of the CCA. As the stenosis
if no previous symptoms can be determined or if symptoms at the bifurcation becomes more severe, the velocity
happened >6 months ago, and ‘symptomatic’ if linked of the ICA velocity increases, which in turn, leads to
with symptoms in the previous 6 months. a higher ICA/CCA PSV ratio (Fig 6-10). To date, there
is a wide range and no internationally accepted standard
IMAGING STUDIES for the gradation of carotid stenosis. The Society of
Radiologists in Ultrasound (SRU) consensus criteria
In patients with stroke or TIA, an urgent imaging are still widely used and recommend PSV cutoff values
139
A B
B
A
"
"
C D
D
C
! !
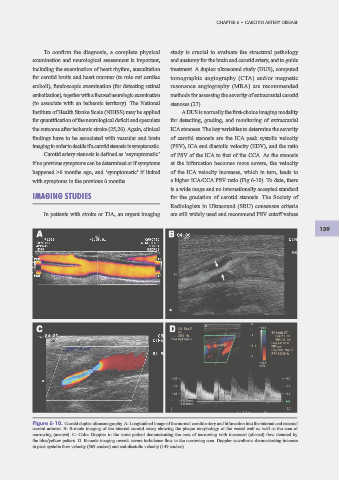
Figure 6-10. Carotid duplex ultrasonography. A: Longitudinal image of the normal carotid artery and bifurcation into the internal and external
carotid arteries. B: B-mode imaging of the internal carotid artery showing the plaque morphology of the vessel wall as well as the area of
narrowing (arrows). C: Color Doppler in the same patient demonstrating the area of narrowing with increased (aliased) f ow denoted by
the blue/yellow pattern. D. B-mode imaging reveals severe turbulence f ow in the narrowing area. Doppler waveforms demonstrating increase
in peak systolic f ow velocity (369 cm/sec) and end-diastolic velocity (149 cm/sec).