Page 7 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 7
CHAPTER 6 • CAROTID ARTERY DISEASE
Middle meningeal artery
Branch of middle
cerebral artery
Middle cerebral artery
Ophthamic artery
Posterior
communicating
artery
Posterior
cerebral
artery
Basilar artery Angular artery
Infraorbital artery
Occipital artery
Collateral
ICA circulation
Maxillar artery Buccal artery occlusion
Vertebral artery Middle Middle
Collateral meningeal
meninigeal
circulation artery
artery
ICA occlusion
ICA
External occlusion
carotid
Common
carotid artery
artery
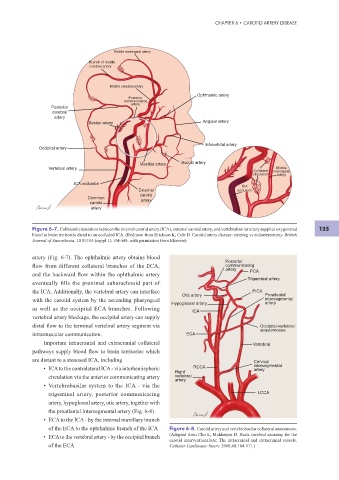
Figure 6-7. Collateral circulation between the internal carotid artery (ICA), external carotid artery, and vertebrobasilar artery supplies oxygenated 135
blood to brain territories distal to an occluded ICA. (Redrawn from Erickson K, Cole D. Carotid artery disease: stenting vs endarterectomy. British
Journal of Anaesthesia. 1010:105 (suppl 1): i34–i49, with permission from Elsevier)
artery (Fig. 6-7). The ophthalmic artery obtains blood
Posterior
f ow from different collateral branches of the ECA, communicating
artery PCA
and the backward f ow within the ophthalmic artery
Trigeminal artery
eventually f lls the proximal subarachnoid part of
the ICA. Additionally, the vertebral artery can interface PICA
Otic artery Proatlantal
with the carotid system by the ascending pharyngeal intersegmental
Hypoglossal artery artery
as well as the occipital ECA branches. Following
ICA
vertebral artery blockage, the occipital artery can supply
distal f ow to the terminal vertebral artery segment via Occipital-vertebral
anastomoses
intramuscular communication. ECA
Important intracranial and extracranial collateral Vertebral
pathways supply blood f ow to brain territories which
are distant to a stenosed ICA, including Cervical
• ICA to the contralateral ICA - via interhemispheric RCCA intersegmental
Right artery
circulation via the anterior communicating artery vertebral
artery
• Vertebrobasilar system to the ICA - via the
trigeminal artery, posterior communicating LCCA
artery, hypoglossal artery, otic artery, together with
the proatlantal intersegmental artery (Fig. 6-8)
• ECA to the ICA - by the internal maxillary branch
of the ECA to the ophthalmic branch of the ICA Figure 6-8. Carotid artery and vertebrobasilar collateral anatomoses.
• ECA to the vertebral artery - by the occipital branch (Adapted from Cho L, Mukherjee D. Basic cerebral anatomy for the
carotid interventionalists: The intracranial and extracranial vessels.
of the ECA Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2006;68:104-111.)