Page 9 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 9
CHAPTER 6 • CAROTID ARTERY DISEASE
to cerebrovascular insuff ciency. Three patterns of large an annual stroke risk of about 2% to 5% for patients
vessel injury are described as; 1) intimal damage with suffering from severe asymptomatic carotid stenosis
mural thrombosis occurring within 5 years of therapy, (ACAS) (3,21). On the opposite side, among symptomatic
2) f brotic occlusion presenting within 10 years, as well as patients (i.e., patients who have had previous stroke or TIA),
3) predisposition to development of atheroma together with the risk of a subsequent stroke increases to 12% - 15%
periarterial f brosis that has a latency of about 20 years (20). during the f rst year and 30% - 35% within 5 years (22).
Radiation-induced atheromatous lesions are similar to usual Besides patient symptoms, annual stroke risk is dependent
atherosclerotic lesions. However, the lesions are clearly on stenosis severity, rate of disease progression, plaque
conf ned to irradiated vessel segments, sparing close morphology, contralateral disease, silent cerebral infarction,
nonirradiated segments, which present in unusual locations collaterals’ extent, and concurrent medical treatment.
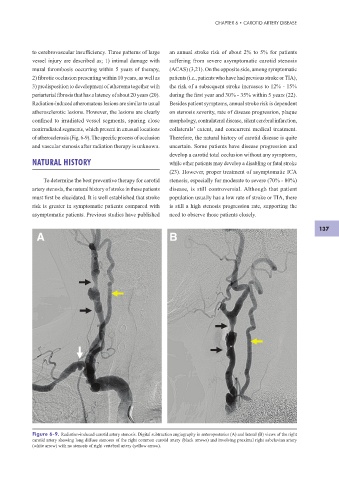
of atherosclerosis (Fig. 6-9). The specif c process of occlusion Therefore, the natural history of carotid disease is quite
and vascular stenosis after radiation therapy is unknown. uncertain. Some patients have disease progression and
develop a carotid total occlusion without any symptoms,
NATURAL HISTORY while other patients may develop a disabling or fatal stroke
(23). However, proper treatment of asymptomatic ICA
To determine the best preventive therapy for carotid stenosis, especially for moderate to severe (70% - 80%)
artery stenosis, the natural history of stroke in these patients disease, is still controversial. Although that patient
must f rst be elucidated. It is well established that stroke population usually has a low rate of stroke or TIA, there
risk is greater in symptomatic patients compared with is still a high stenosis progression rate, supporting the
asymptomatic patients. Previous studies have published need to observe those patients closely.
137
A A B B
Figure 6-9. Radiation-induced carotid artery stenosis. Digital subtraction angiography in anteroposterior (A) and lateral (B) views of the right
carotid artery showing long diffuse stenoses of the right common carotid artery (black arrows) and involving proximal right subclavian artery
(white arrow) with no stenosis of right vertebral artery (yellow arrow).