Page 6 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 6
CAROTID AND PERIPHERAL VASCULAR INTERVENTIONS: STEP-BY-STEP
Anterior
communicating
artery Anterior
Middle Recurrent
cerebral artery of cerebral
artery Heubner artery
Ophthalmic
artery
Lenticulostriate
arteries
Anteromedial
central
Internal arteries Anterior
carotid Circle of choroidal
artery Willis artery
Posteromedial
Posterior central Posterior
cerebral arteries communicating
artery
artery
Superior
Pontine cerebellar
arteries artery
Basilar
Labyrinthine artery
(or internal Anterior
auditory) artery inferior
cerebellar
artery
Posterior
inferior
cerebellar
artery
Vertebral
134 artery
Anterior
spinal
artery
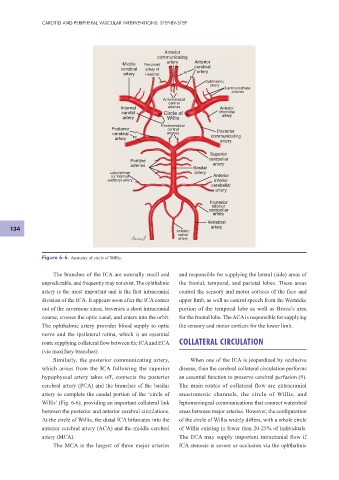
Figure 6-6. Anatomy of circle of Willis.
The branches of the ICA are normally small and and responsible for supplying the lateral (side) areas of
unpredictable, and frequently may not exist. The ophthalmic the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes. These areas
artery is the most important and is the f rst intracranial control the sensory and motor cortices of the face and
division of the ICA. It appears soon after the ICA comes upper limb, as well as control speech from the Wernicke
out of the cavernous sinus, traverses a short intracranial portion of the temporal lobe as well as Broca’s area
course, crosses the optic canal, and enters into the orbit. for the frontal lobe. The ACA is responsible for supplying
The ophthalmic artery provides blood supply to optic the sensory and motor cortices for the lower limb.
nerve and the ipsilateral retina, which is an essential
route supplying collateral f ow between the ICA and ECA COLLATERAL CIRCULATION
(via maxillary branches).
Similarly, the posterior communicating artery, When one of the ICA is jeopardized by occlusive
which arises from the ICA following the superior disease, then the cerebral collateral circulation performs
hypophyseal artery takes off, connects the posterior an essential function to preserve cerebral perfusion (9).
cerebral artery (PCA) and the branches of the basilar The main routes of collateral f ow are extracranial
artery to complete the caudal portion of the ‘circle of anastomotic channels, the circle of Willis, and
Willis’ (Fig. 6-6), providing an important collateral link leptomeningeal communications that connect watershed
between the posterior and anterior cerebral circulations. areas between major arteries. However, the conf guration
At the circle of Willis, the distal ICA bifurcates into the of the circle of Willis widely differs, with a whole circle
anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and the middle cerebral of Willis existing in fewer than 20-25% of individuals.
artery (MCA). The ECA may supply important intracranial f ow if
The MCA is the largest of three major arteries ICA stenosis is severe or occlusion via the ophthalmic