Page 3 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 3
CHAPTER 6 • CAROTID ARTERY DISEASE
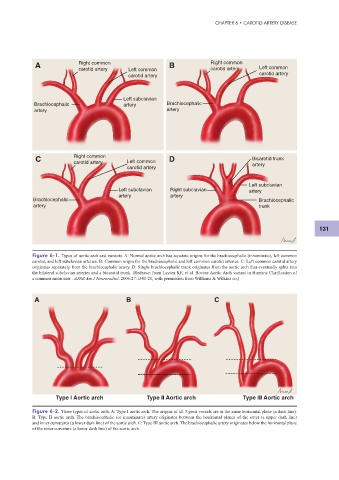
A Right common B Right common
carotid artery Left common carotid artery Left common
carotid artery carotid artery
Left subclavian
Brachiocephalic artery Brachiocephalic
artery artery
C Right common D Bicarotid trunk
carotid artery Left common artery
carotid artery
Left subclavian
Left subclavian Right subclavian artery
artery artery
Brachiocephalic Brachiocephalic
artery trunk
131
Figure 6-1. Types of aortic arch and variants. A: Normal aortic arch has separate origins for the brachiocephalic (innominate), left common
carotid, and left subclavian arteries. B: Common origin for the brachiocephalic and left common carotid arteries. C: Left common carotid artery
originates separately from the brachiocephalic artery. D: Single brachiocephalic trunk originates from the aortic arch that eventually splits into
the bilateral subclavian arteries and a bicarotid trunk. (Redrawn from Layton KF, et al. Bovine Aortic Arch variant in Humans Clarif cation of
a common misnomer . AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006:27:1541-21, with permission from Williams & Wilkins co.)
A B C
Type I Aortic arch Type II Aortic arch Type III Aortic arch
Figure 6-2. Three types of aortic arch. A: Type I aortic arch. The origins of all 3 great vessels are in the same horizontal plane (a dash line).
B: Type II aortic arch. The brachiocephalic (or innominate) artery originates between the horizontal planes of the outer (a upper dash line)
and inner curvatures (a lower dash line) of the aortic arch. C: Type III aortic arch. The brachiocephalic artery originates below the horizontal plane
of the inner curvature (a lower dash line) of the aortic arch.