Page 4 - Carotid and peripheral vascular interventions textbook
P. 4
CAROTID AND PERIPHERAL VASCULAR INTERVENTIONS: STEP-BY-STEP
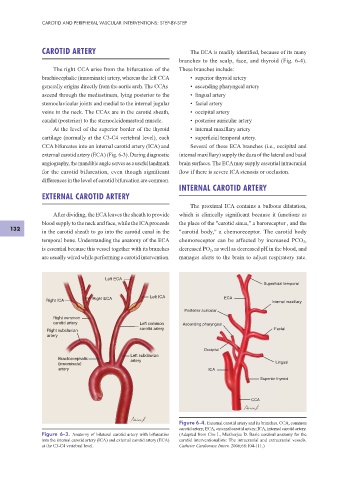
CAROTID ARTERY The ECA is readily identif ed, because of its many
branches to the scalp, face, and thyroid (Fig. 6-4).
The right CCA arise from the bifurcation of the These branches include:
brachiocephalic (innominate) artery, whereas the left CCA • superior thyroid artery
generally origins directly from the aortic arch. The CCAs • ascending pharyngeal artery
ascend through the mediastinum, lying posterior to the • lingual artery
sternoclavicular joints and medial to the internal jugular • facial artery
veins in the neck. The CCAs are in the carotid sheath, • occipital artery
caudal (posterior) to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. • posterior auricular artery
At the level of the superior border of the thyroid • internal maxillary artery
cartilage (normally at the C3-C4 vertebral level), each • superf cial temporal artery.
CCA bifurcates into an internal carotid artery (ICA) and Several of these ECA branches (i.e., occipital and
external carotid artery (ECA) (Fig. 6-3). During diagnostic internal maxillary) supply the dura of the lateral and basal
angiography, the mandible angle serves as a useful landmark brain surfaces. The ECA may supply essential intracranial
for the carotid bifurcation, even though signif cant f ow if there is severe ICA stenosis or occlusion.
differences in the level of carotid bifurcation are common.
INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY
EXTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY
The proximal ICA contains a bulbous dilatation,
After dividing, the ECA leaves the sheath to provide which is clinically signif cant because it functions as
blood supply to the neck and face, while the ICA proceeds the place of the "carotid sinus," a baroreceptor , and the
132
in the carotid sheath to go into the carotid canal in the "carotid body," a chemoreceptor. The carotid body
temporal bone. Understanding the anatomy of the ECA chemoreceptor can be affected by increased PCO 2,
is essential because this vessel together with its branches decreased PO 2, as well as decreased pH in the blood, and
are usually wired while performing a carotid intervention. manages alerts to the brain to adjust respiratory rate.
Left ECA
Superficial temporal
Right ECA Left ICA ECA
Right ICA Internal maxillary
Posterior auricular
Right common
carotid artery Left common Ascending pharyngeal
Right subclavian carotid artery Facial
artery
Occipital
Left subclavian
Brachiocephalic artery
(innominate) Lingual
artery ICA
Superior thyroid
CCA
Figure 6-4. External carotid artery and its branches. CCA, common
carotid artery; ECA, external carotid artery; ICA, internal carotid artery.
Figure 6-3. Anatomy of bilateral carotid artery with bifurcation (Adapted from Cho L, Mukherjee D. Basic cerebral anatomy for the
into the internal carotid artery (ICA) and external carotid artery (ECA) carotid interventionalists: The intracranial and extracranial vessels.
at the C3-C4 vertebral level. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2006;68:104-111.)